Algorithmic Amplification of Politics on Twitter
→
Brown Data Science Initiative 2022
Measuring disparate outcomes of content recommendation algorithms with distributional inequality metrics
→
In recent years, many examples of the potential harms caused by machine learning systems have come to the forefront. Practitioners in the field of algorithmic bias and fairness have developed a suite of metrics to capture one aspect of these harms.
From Optimizing Engagement to Measuring Value
→
Most recommendation engines today are based on predicting user engagement, e.g. predicting whether a user will click on an item or not. However, there is potentially a large gap between engagement signals and a desired notion of "value" that is worth optimizing for.
Assessing demographic bias in named entity recognition
→
Named Entity Recognition (NER) is often the first step towards automated Knowledge Base (KB) generation from raw text. In this work, we assess the bias in various Named Entity Recognition (NER) systems for English across different demographic groups with synthetically generated corpora.
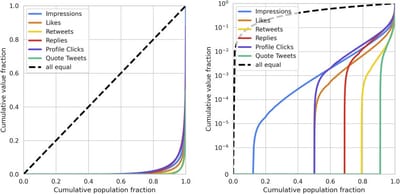
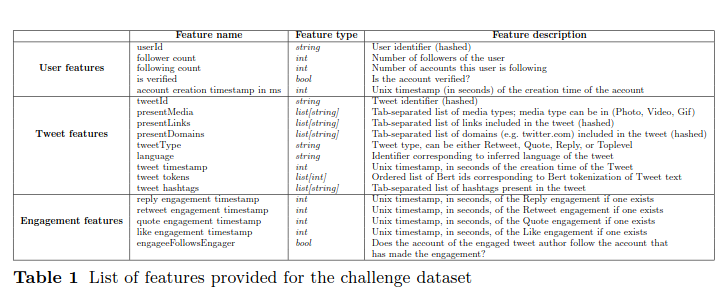
Privacy-Aware Recommender Systems Challenge on Twitter's Home Timeline
→
Recommender systems constitute the core engine of most social network platforms, aiming to maximize user satisfaction along with other key business objectives. The implicit feedback provided by users on Tweets through their engagements on the Home Timeline has only been explored to a limited extent.
Responsible Recommendation
→
RecSys conference panel 2019
Why Monads?
→
Building intuition on why monads are useful will help better understand what they are as well.